|
Green solar products Pre-heating solar water heater
+ Stainless inner tank Split & Pressure Solar System
+ Solar System with stainless inner tank + Solar System with porcelain enamel tank Solar collector
+ Heat Pipe solar collector + Vacuum tube solar collector + Flat panel solar collector Solar project
+ Solar pool heating system + Solar space heating system + Solar water heating for villa + Others Accessories
+ solar water heater accessories + solar controller Home Appliance Products
Contact Us :
Factory in China Tel : 86-519-85256385 Fax : 86-519-85256385 Cell : 86-13861291747 Email : timsolar@vip.163.com timsolar2012@gmail.com Contact : Mr.Tim Liu Site : www.greensolarchina.com Company in Greece Tel : 30 2310 953421 Fax : 30 2310 953422 Cell : 30 6977 353638 Email : info@green-solar.net Site: www.green-solar.net |
Solar Space Heating System

Solar Space Heating
If you want to heat your home with solar energy, you will need to decide whether you want an active or a passive system. Although passive systems are popular because of their simplicity, they are sometimes impractical to install (retrofit) in an existing home, particularly if much of the site is shaded. Active systems are often more practical for such applications. Choosing the proper solar energy system depends on varying conditions such as the site, design, and heating needs of the house. Although active systems are typically installed on the roof, they can be ground or wall-mounted to take advantage of the availability of solar radiation. You may prefer the aesthetics of a passive solar sunspace instead of rooftop collectors. If you are unsure about what type of solar energy system to install, contact a solar energy specialist or engineer. No matter what system you choose, you should learn about it before making a purchase. How Much Heat Should Active Systems Provide?
Active solar energy systems are usually designed to provide 40% to 80% of the home's heating needs. Systems providing less than 40% of the heat needed for a home are rarely cost-effective except when using air panels for walls, window boxes, and other collectors that heat one room and require no heat storage. The size of the active system helps determine how much heat it can provide. If you are planning to purchase a system, you must determine how large your system should be. Computer software is often used to properly size active systems. (For information on solar computer software, contact the EREC.) 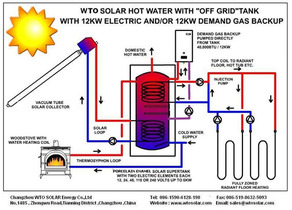
Back-up Heating-A Supplement for Active Systems
Most building codes and mortgage lenders require a back-up heating system for houses heated with solar energy. Back-up systems supply heat when, for example, there are long periods of cloudy weather. Back-up systems range from a wood stove to a conventional heating system. Positioning Collectors to Perform Optimally In general, the optimum collector orientation is true south. True south is the highest apparent point in the sky that the sun reaches during the day. (True south should not be confused with magnetic south as indicated on a compass.) Collector orientation may deviate up to 20° from true south without significantly reducing the performance of the system. Collectors should be tilted at an angle equal to your latitude plus 15°. A collector receives the most solar radiation between 9:00 am and 3:00 pm. Trees, buildings, hills, or other obstructions that shade collectors reduce their ability to collect solar radiation. Even partial shading will affect performance and increase the payback period of the system. You can position collectors in different locations. Collectors usually receive the most sunlight when placed in rows on the roof. In some cases, however, the roof may be too shady. If the roof does not receive enough sunlight, you may want to mount the collectors on a supporting structure on the ground, or in rows on the south wall of the house, where there is enough sunlight for the collectors to perform satisfactorily. Collectors mounted on the ground or on an exterior wall perform almost as well as those mounted on most roofs. |
| Green Solar New Energy Co. Ltd |
|
- HOME
- SERVICES
-
SOLAR PRODUCTS
- Low pressure stainless inner tank >
- Low pressure porcelain enamel inner tank >
- Compact & pressue stainless inner tank >
- Compact & pressue porcelain enamel inner tank >
- Pre-heating solar water heater >
- Split & Pressure Solar System with stainless inner tank >
- Split & Pressure Solar System with porcelain enamel inner tank >
- Heat Pipe solar collector >
- vacuum tube solar collector >
- Flat panel solar collector >
- Solar project >
- APPLIANCE PRODUCTS
- Accessories
- DOWNLOADS
- GALLERY
- CONTACT US



